中国沙漠 ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (2): 35-47.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2023.00100
郭源上1,2( ), 何明珠3, 刘建兵2, 张汐2, 谷守江2, 武文进2, 高立博2, 冯晓莉2, 韩国君1(
), 何明珠3, 刘建兵2, 张汐2, 谷守江2, 武文进2, 高立博2, 冯晓莉2, 韩国君1( )
)
收稿日期:2023-05-29
修回日期:2023-07-13
出版日期:2024-03-20
发布日期:2024-03-19
通讯作者:
韩国君
作者简介:韩国君(E-mail: hangj@gsau.edu.cn)基金资助:
Yuanshang Guo1,2( ), Mingzhu He3, Jianbing Liu2, Xi Zhang2, Shoujiang Gu2, Wenjin Wu2, Libo Gao2, Xiaoli Feng2, Guojun Han1(
), Mingzhu He3, Jianbing Liu2, Xi Zhang2, Shoujiang Gu2, Wenjin Wu2, Libo Gao2, Xiaoli Feng2, Guojun Han1( )
)
Received:2023-05-29
Revised:2023-07-13
Online:2024-03-20
Published:2024-03-19
Contact:
Guojun Han
摘要:
矿山遗迹地的生态修复是促进人与自然和谐共生、实现绿色低碳发展的重要举措。干旱区矿山遗迹地立地条件差,植被覆盖率低,采矿活动造成的土壤侵蚀强烈,确定科学合理的恢复模式是生态修复成功与否的关键。以宁夏中卫市的典型石灰岩矿山遗迹地为研究对象,通过对比7种生态修复植物在不同土壤基质重构措施下的土壤温、湿度和有机质,以及植物的存活率和新生枝相对生长速率(Relative growth rate of new shoots, RGRs)等指标,筛选出适宜干旱区石灰岩矿山遗迹地生态修复的最优模式,构建了土壤改良-植被重建联合的生态恢复方案。结果表明:(1)土壤基质重构措施是石灰岩矿山生态修复的前提条件,有效地改善了植物定植环境,不同土壤基质重构模式的植物存活率表现为:土+有机肥>砂+土+有机肥>砂+土+复合肥;(2)土壤有机质的范围为0.56~2.84 g·kg-1,植物种和土壤基质及二者的交互作用对土壤有机质含量具有极显著影响(P<0.001);(3)RGRs的范围为1.51~1.87 mm·cm-1·month-1,不同植物种的RGRs存在显著性差异;(4)通过系统聚类分析得到本研究区最适宜的生态修复模式为砂+土+有机肥(沙拐枣或短穗柽柳)。本研究从土壤改良-植被重建角度提出的联合生态修复方案可为干旱区矿山生态修复提供理论依据和实践参考。
中图分类号:
郭源上, 何明珠, 刘建兵, 张汐, 谷守江, 武文进, 高立博, 冯晓莉, 韩国君. 干旱区石灰岩矿山遗迹地生态修复模式对比研究[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(2): 35-47.
Yuanshang Guo, Mingzhu He, Jianbing Liu, Xi Zhang, Shoujiang Gu, Wenjin Wu, Libo Gao, Xiaoli Feng, Guojun Han. A comparative study of ecological remediation approaches in arid limestone mining remnants[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2024, 44(2): 35-47.
| 处理 | SiO2/% | Al2O3/% | TFe2O3/% | CaO/% | MgO/% | K2O/% | Na2O/% | 其他/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 砂+土(南边坡) | 29.94 | 6.94 | 3.25 | 22.05 | 7.46 | 1.66 | 0.21 | 28.49 |
| 砂+土(西边坡) | 31.94 | 6.71 | 2.79 | 23.93 | 5.07 | 1.41 | 0.27 | 27.88 |
| 砂+土(短穗柽柳) | 26.39 | 6.37 | 2.73 | 24.26 | 7.94 | 1.48 | 0.23 | 30.60 |
| 砂+土(蒙古莸) | 33.99 | 8.77 | 3.60 | 19.53 | 6.57 | 1.95 | 0.29 | 25.30 |
| 砂+土(四翅滨藜) | 15.75 | 3.03 | 1.74 | 30.42 | 10.54 | 0.64 | 0.15 | 37.73 |
| 砂+土(柠条) | 23.83 | 4.21 | 2.07 | 27.29 | 7.95 | 0.91 | 0.26 | 33.48 |
表1 研究区岩性
Table 1 Lithology of the study area
| 处理 | SiO2/% | Al2O3/% | TFe2O3/% | CaO/% | MgO/% | K2O/% | Na2O/% | 其他/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 砂+土(南边坡) | 29.94 | 6.94 | 3.25 | 22.05 | 7.46 | 1.66 | 0.21 | 28.49 |
| 砂+土(西边坡) | 31.94 | 6.71 | 2.79 | 23.93 | 5.07 | 1.41 | 0.27 | 27.88 |
| 砂+土(短穗柽柳) | 26.39 | 6.37 | 2.73 | 24.26 | 7.94 | 1.48 | 0.23 | 30.60 |
| 砂+土(蒙古莸) | 33.99 | 8.77 | 3.60 | 19.53 | 6.57 | 1.95 | 0.29 | 25.30 |
| 砂+土(四翅滨藜) | 15.75 | 3.03 | 1.74 | 30.42 | 10.54 | 0.64 | 0.15 | 37.73 |
| 砂+土(柠条) | 23.83 | 4.21 | 2.07 | 27.29 | 7.95 | 0.91 | 0.26 | 33.48 |
| 土壤基质 | 粒级 | 平均值±标准差/% | 土壤基质 | 粒级 | 平均值±标准差/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 砂+土 | 石砾 | 42.60±7.98a | 砂+土+有机肥 | 石砾 | 45.51±7.89a |
| 粗砂 | 21.60±4.42a | 粗砂 | 21.32±6.23a | ||
| 细砂 | 20.00±5.44a | 细砂 | 17.96±6.08a | ||
| 粉砂 | 15.17±2.53a | 粉砂 | 14.09±4.03ab | ||
| 黏粒 | 4.66±0.58a | 黏粒 | 4.34±1.07ab | ||
| 砂+土+复合肥 | 石砾 | 48.25±8.51a | 土+有机肥 | 石砾 | 42.83±6.70a |
| 粗砂 | 19.19±2.92a | 粗砂 | 20.86±3.64a | ||
| 细砂 | 20.52±7.39a | 细砂 | 20.02±3.52a | ||
| 粉砂 | 11.14±0.24b | 粉砂 | 15.16±2.27ab | ||
| 黏粒 | 3.06±0.93b | 黏粒 | 4.78±0.75a |
表2 研究区土壤粒级分布
Table 2 Soil separate of the study area
| 土壤基质 | 粒级 | 平均值±标准差/% | 土壤基质 | 粒级 | 平均值±标准差/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 砂+土 | 石砾 | 42.60±7.98a | 砂+土+有机肥 | 石砾 | 45.51±7.89a |
| 粗砂 | 21.60±4.42a | 粗砂 | 21.32±6.23a | ||
| 细砂 | 20.00±5.44a | 细砂 | 17.96±6.08a | ||
| 粉砂 | 15.17±2.53a | 粉砂 | 14.09±4.03ab | ||
| 黏粒 | 4.66±0.58a | 黏粒 | 4.34±1.07ab | ||
| 砂+土+复合肥 | 石砾 | 48.25±8.51a | 土+有机肥 | 石砾 | 42.83±6.70a |
| 粗砂 | 19.19±2.92a | 粗砂 | 20.86±3.64a | ||
| 细砂 | 20.52±7.39a | 细砂 | 20.02±3.52a | ||
| 粉砂 | 11.14±0.24b | 粉砂 | 15.16±2.27ab | ||
| 黏粒 | 3.06±0.93b | 黏粒 | 4.78±0.75a |
| 差异源 | 平方和 | df | 均方 | F | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 植物 | 8.45 | 6 | 1.41 | 31.00 | <0.001 |
| 土壤基质改良 | 2.99 | 3 | 1.00 | 21.93 | <0.001 |
| 植物×土壤基质改良 | 6.83 | 15 | 0.46 | 10.02 | <0.001 |
表3 植物和土壤基质对土壤有机质影响的双因素方差分析结果
Table 3 Two-way analysis of variance results of the effects of plant and soil matrix on soil organic matter
| 差异源 | 平方和 | df | 均方 | F | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 植物 | 8.45 | 6 | 1.41 | 31.00 | <0.001 |
| 土壤基质改良 | 2.99 | 3 | 1.00 | 21.93 | <0.001 |
| 植物×土壤基质改良 | 6.83 | 15 | 0.46 | 10.02 | <0.001 |
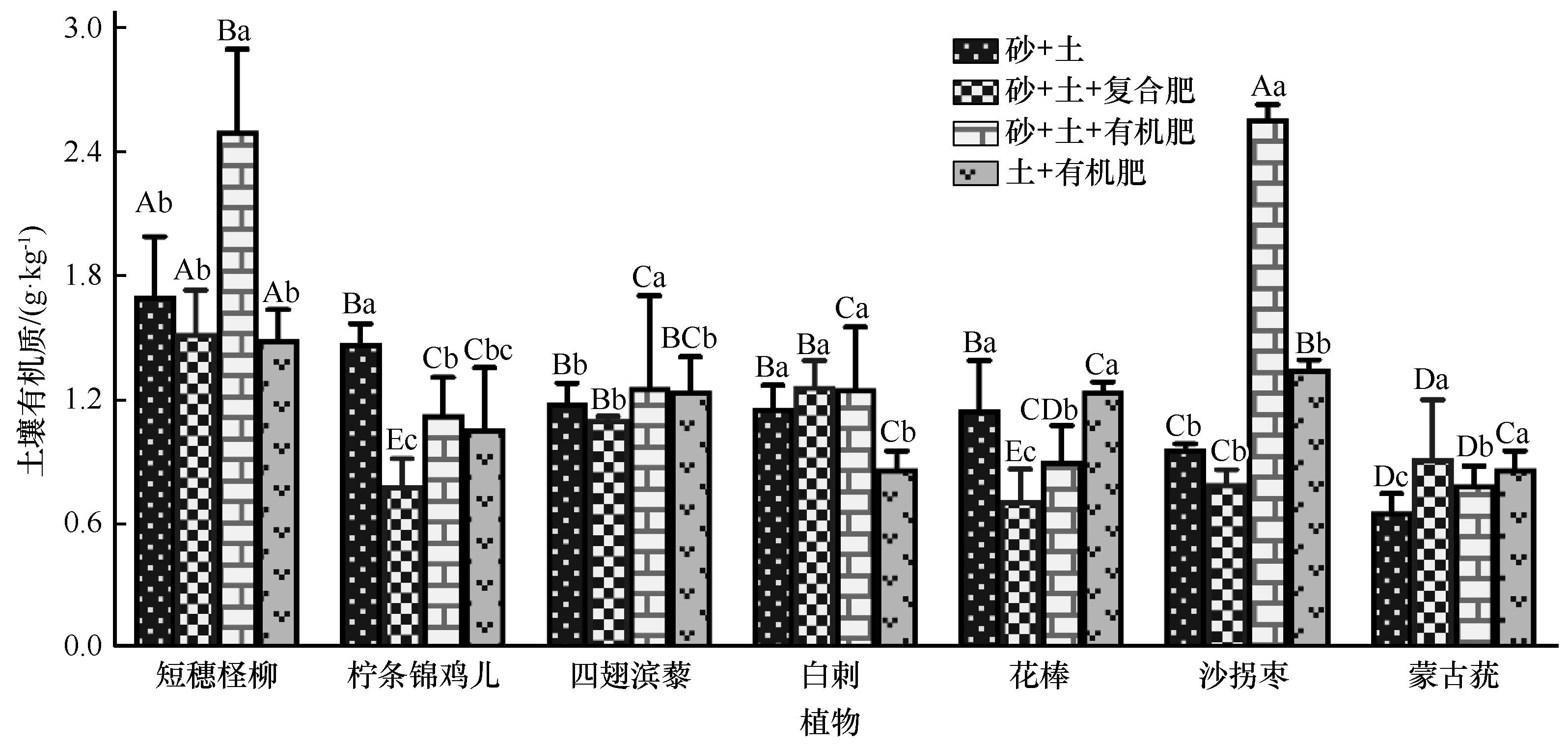
图6 不同植物和土壤基质的土壤有机质注:不同大写字母表示同一土壤基质不同植物根区土壤有机质差异显著(P<0.05),不同小写字母表示同一植物不同土壤基质土壤有机质差异显著(P<0.05)
Fig.6 Soil organic matter of different plants and soil substrates
| 土壤 基质 | 植物 | 存活率/% | 土壤 基质 | 植物 | 存活率/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 砂+土 | 短穗柽柳 | 98.57 | 砂+土+ 有机肥 | 短穗柽柳 | 99.40 |
| 白刺 | 97.69 | 白刺 | 98.77 | ||
| 沙拐枣 | 96.09 | 沙拐枣 | 96.03 | ||
| 蒙古莸 | 93.98 | 柠条锦鸡儿 | 92.73 | ||
| 花棒 | 84.82 | 花棒 | 87.78 | ||
| 柠条锦鸡儿 | 84.35 | 蒙古莸 | 82.01 | ||
| 四翅滨藜 | 63.39 | 四翅滨藜 | 71.43 | ||
| 砂+土+ 复合肥 | 白刺 | 97.73 | 土+ 有机肥 | 白刺 | 100.00 |
| 短穗柽柳 | 96.46 | 沙拐枣 | 99.11 | ||
| 沙拐枣 | 95.81 | 短穗柽柳 | 98.30 | ||
| 柠条锦鸡儿 | 92.52 | 柠条锦鸡儿 | 94.62 | ||
| 蒙古莸 | 86.55 | 蒙古莸 | 89.23 | ||
| 花棒 | 84.62 | 花棒 | 79.52 | ||
| 四翅滨藜 | 68.37 | 四翅滨藜 | 75.68 |
表4 植物存活率
Table 4 Plant survival rate
| 土壤 基质 | 植物 | 存活率/% | 土壤 基质 | 植物 | 存活率/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 砂+土 | 短穗柽柳 | 98.57 | 砂+土+ 有机肥 | 短穗柽柳 | 99.40 |
| 白刺 | 97.69 | 白刺 | 98.77 | ||
| 沙拐枣 | 96.09 | 沙拐枣 | 96.03 | ||
| 蒙古莸 | 93.98 | 柠条锦鸡儿 | 92.73 | ||
| 花棒 | 84.82 | 花棒 | 87.78 | ||
| 柠条锦鸡儿 | 84.35 | 蒙古莸 | 82.01 | ||
| 四翅滨藜 | 63.39 | 四翅滨藜 | 71.43 | ||
| 砂+土+ 复合肥 | 白刺 | 97.73 | 土+ 有机肥 | 白刺 | 100.00 |
| 短穗柽柳 | 96.46 | 沙拐枣 | 99.11 | ||
| 沙拐枣 | 95.81 | 短穗柽柳 | 98.30 | ||
| 柠条锦鸡儿 | 92.52 | 柠条锦鸡儿 | 94.62 | ||
| 蒙古莸 | 86.55 | 蒙古莸 | 89.23 | ||
| 花棒 | 84.62 | 花棒 | 79.52 | ||
| 四翅滨藜 | 68.37 | 四翅滨藜 | 75.68 |
| 序号 | 土壤有机质 /(g·kg-1) | 存活率 /% | RGRs /(mm·cm-1·month-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 第Ⅰ类 | 1.27±0.33b | 95±6a | 1.26±0.04b |
| 第Ⅱ类 | 1.14±0.13bc | 74±8b | 1.45±0.08a |
| 第Ⅲ类 | 0.88±0.21c | 91±6a | 1.51±0.04a |
| 第Ⅳ类 | 2.53±0.04a | 98±2a | 1.25±0.07b |
表5 各类群指标
Table 5 Indicators of different groups
| 序号 | 土壤有机质 /(g·kg-1) | 存活率 /% | RGRs /(mm·cm-1·month-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 第Ⅰ类 | 1.27±0.33b | 95±6a | 1.26±0.04b |
| 第Ⅱ类 | 1.14±0.13bc | 74±8b | 1.45±0.08a |
| 第Ⅲ类 | 0.88±0.21c | 91±6a | 1.51±0.04a |
| 第Ⅳ类 | 2.53±0.04a | 98±2a | 1.25±0.07b |
| 1 | 农仕华,韦佳伟,蒙颖森.石灰岩矿床不同资源储量估算方法对比分析[J].西部探矿工程,2022,34(9):120-122. |
| 2 | Li J G, Li Z X, Brandis K J,et al.Tracing geochemical pollutants in stream water and soil from mining activity in an alpine catchment[J].Chemosphere,2020,242:125167. |
| 3 | Shi J, Du P, Luo H L,et al.Soil contamination with cadmium and potential risk around various mines in China during 2000-2020[J].Journal of Environmental Management,2022,310:114509. |
| 4 | Nguyen T H, Won S, Ha M G,et al.Bioleaching for environmental remediation of toxic metals and metalloids:a review on soils,sediments,and mine tailings[J].Chemosphere,2021,282:131108. |
| 5 | Xu Q, Xia G Z, Wei Y,et al.Responses of vegetation and soil to artificial restoration measures in abandoned gold mining areas in altai mountain,northwest China[J].Diversity-Basel,2022,14(6):427. |
| 6 | Wang C X, Liu X, Wu J C,et al.Planning a water-constrained ecological restoration pattern to enhance sustainable landscape management in drylands[J].Journal of Environmental Management,2023,335:117514. |
| 7 | Bai D S, Yang X, Lai J L,et al.In situ restoration of soil ecological function in a coal gangue reclamation area after 10 years of elm/poplar phytoremediation[J].Journal of Environmental Management,2022,305:114400. |
| 8 | Shi Y F, Zang Y F, Yang H H,et al.Biochar enhanced phytostabilization of heavy metal contaminated mine tailings:a review[J].Frontiers in Environmental Science,2022,10:1044921. |
| 9 | Liu J, Zhang S W, Li E W,et al.Effects of cubic ecological restoration of mining wasteland and the preferred restoration scheme[J].Science of the Total Environment,2022,851(1):158155. |
| 10 | Gairola S U, Bahuguna R, Bhatt S S.Native plant species:a tool for restoration of mined lands[J].Journal of Soil Science and Plant Nutrition,2023,23(2):1438-1448. |
| 11 | Laffont-Schwob I, Rabier J, Masotti V,et al.Functional Trait-Based screening of Zn-Pb tolerant wild plant species at an abandoned mine site in Gard (France) for rehabilitation of mediterranean Metal-Contaminated soils[J].International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health,2020,17(15):5506. |
| 12 | 何明珠,胡天光,程斌让,等.干旱区尾矿污染环境的植物修复技术研究进展[J].中国沙漠,2014,34(5):1329-1336. |
| 13 | Konig L A, Medina-Vega J A, Longo R M,et al.Restoration success in former Amazonian mines is driven by soil amendment and forest proximity[J].Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B-Biological Sciences,2023,378(1867):20210086. |
| 14 | Bateman A M, Erickson T E, Merritt D J,et al.Native plant diversity is a stronger driver for soil quality than inorganic amendments in semi-arid post-mining rehabilitation[J].Geoderma,2021,394:115001. |
| 15 | Qian L, Lin H, Li B,et al.Physicochemical characteristics and microbial communities of rhizosphere in complex amendment-assisted soilless revegetation of gold mine tailings[J].Chemosphere,2023,320:138052. |
| 16 | Wang X Y, Li Y, Wei Y,et al.Effects of fertilization and reclamation time on soil bacterial communities in coal mining subsidence areas[J].Science of the Total Environment,2020,739:139882. |
| 17 | Ginocchio R, de la Fuente L M, Orrego F,et al.A novel fast-vegetative propagation technique of the pioneer shrub Baccharis linearis on mine tailings by adding compost[J].International Journal of Phytoremediation,2021,23(11):1169-1174. |
| 18 | Hussain Z, Alam M, Khan M A,et al.Bioaccumulation of potentially toxic elements in spinach grown on contaminated soils amended with organic fertilizers and their subsequent human health risk[J].Arabian Journal of Geosciences,2020,13(18):945. |
| 19 | Wang L L, Wang F, Wang S F,et al.Analysis of differences in chemical properties of reconstructed soil under different proportions of topsoil substitute materials[J].Environmental Science and Pollution Research,2021,28(24):31230-31245. |
| 20 | Zhu Q, Hu Z Q, Liu X R,et al.Topsoil alternatives selection for surface coal-mined land reclamation in Inner Mongolia,China:an experimental study[J].International Journal of Mining Reclamation and Environment,2021,35(6):421-434. |
| 21 | Lebrun M, Nandillon R, Miard F S,et al.Application of amendments for the phytoremediation of a former mine technosol by endemic pioneer species:alder and birch seedlings[J].Environmental Geochemistry and Health,2021,43(1):77-89. |
| 22 | Pérez R, Tapia Y, Antilén M,et al.Interactive effect of compost application and inoculation with the fungus Claroideoglomus claroideum in Oenothera picensis plants growing in mine tailings[J].Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety,2021,208:111495. |
| 23 | Peco J D, Higueras P, Campos J A,et al.Abandoned mine lands reclamation by plant remediation technologies[J].Sustainability,2021,13(12):6555. |
| 24 | 武万里,程雅茹,马宁.宁夏高速公路横风分布特征及风险分析[J/OL].宁夏大学学报(自然科学版):1-6[2023-05-03].. |
| 25 | 张泽瑾,李晓攀,杨苑,等.中卫市沙尘污染天气分型及气象条件特征分析[J].农业科技与信息,2022(5):40-44. |
| 26 | 鲍士旦.土壤农化分析[M].北京:中国农业出版社,2000. |
| 27 | Mau V, Arye G, Gross A.Poultry litter hydrochar as an amendment for sandy soils[J].Journal of Environmental Management,2020,271:110959. |
| 28 | Shan Y Y, Li G, Bai Y G,et al.Effects of different improvement measures on hydrothermal carbon and cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) yield in saline-alkali soil[J].Applied Ecology and Environmental Research,2022,20(2):1821-1835. |
| 29 | Zhang Y, Zhang M J, Qu D Y,et al.Water use characteristics of different pioneer shrubs at different ages in western Chinese Loess Plateau:evidence from delta H-2 offset correction[J].Journal of Arid Land,2022,14(6):653-672. |
| 30 | Ebmeyer H, Hoffmann C.Water use efficiency of sugar beet genotypes:a relationship between growth rates and water consumption[J].Journal of Agronomy and Crop Science,2022,208(1):28-39. |
| 31 | 付鹏程,胡广录,巩炜,等.河西走廊沙漠-绿洲过渡带固沙植物根区土壤物理性质及持水特性[J].土壤通报,2021,52(4):811-820. |
| 32 | Luo Z T, Niu J Z, He S Q,et al.Linking roots,preferential flow,and soil moisture redistribution in deciduous and coniferous forest soils[J].Journal of Soils and Sediments,2023,23(3):1524-1538. |
| 33 | Ma X F, Zhu J T, Wang Y,et al.Variations in water use strategies of sand-binding vegetation along a precipitation gradient in sandy regions,northern China[J].Journal of Hydrology,2021,600:126539. |
| 34 | Yakupoglu G, Saltali K, Rodrigo-Comino J,et al.Manure effect on Soil-Plant interactions in capia pepper crops under semiarid climate conditions[J].Sustainability,2022,14(20):13695. |
| 35 | He M Z, Ji X B, Bu D S,et al.Cultivation effects on soil texture and fertility in an arid desert region of northwestern China[J].Journal of Arid Land,2020,12(4):701-715. |
| 36 | 王玉珍,黄晓,蔡丽平,等.不同温度条件下土壤颗粒组成对宽叶雀稗种子发芽与幼苗生长的影响[J].草业学报,2018,27(9):45-55. |
| 37 | 马赟花,冯图,李仰征,等.沙棘(Hippophae rhamnoides)对经客土改良石漠化土壤的适应性[J].中国沙漠,2021,41(1):228-233. |
| 38 | 李端,司建华,李继彦,等.胡杨(Populus euphratica)对盐胁迫和干旱胁迫的生理响应特征[J].中国沙漠,2023,43(2):205-215. |
| 39 | 王雨,刘振婷,高广磊,等.干旱胁迫下枯草芽孢杆菌(Bacillus subtilis)对柠条(Caragana korshinskii)和沙冬青(Ammopiptanthus mongolicus)种子萌发及幼苗生长的影响[J].中国沙漠,2022,42(5):73-81. |
| 40 | Hayyat M U, Siddiq Z, Mahmood R,et al.Limestone quarry waste promotes the growth of two native woody angiosperms[J].Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution,2021,9:637833. |
| 41 | Heiskanen J, Ruhanen H, Hagner M.Effects of compost,biochar and ash mixed in till soil cover of mine tailings on plant growth and bioaccumulation of elements:a growing test in a greenhouse[J].Heliyon,2022,8(2):e08838. |
| 42 | 鲁艳,李新荣,何明珠,等.重金属对盐生草光合生理生长特性的影响[J].西北植物学报,2011,31(2):370-376. |
| 43 | 徐慧全,王立,冯宜明,等.重金属在不同温度和光照下对骆驼蓬种子萌发特征的影响[J].水土保持通报,2012,32(1):33-37. |
| 44 | Long L L, Liu Y, Chen X Y,et al.Analysis of spatial variability and influencing factors of soil nutrients in western China:a case study of the Daliuta mining area[J].Sustainability,2022,14(5):2793. |
| 45 | 李圆宾,李鹏,王舒华,等.稻麦轮作体系下有机肥施用对作物产量和土壤性质影响的整合分析[J].应用生态学报,2021,32(9):3231-3239. |
| 46 | Chen Y H, Zhang S Y, Du S F,et al.Analysis of amino acids in the roots of Tamarix ramosissima by application of exogenous potassium (K+) under NaCl stress[J].International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2022,23(16):9331. |
| 47 | Hu J, Hu X K, Duan H R,et al.Na+ and K+ homeostasis is important for salinity and drought tolerance of calligonum mongolicum[J].Pakistan Journal of Botany,2021,53(6):1927-1934. |
| 48 | 何明珠,王辉,陈智平.荒漠植物持水力研究[J].中国沙漠,2006,26(3):403-408. |
| 49 | Li Z K, Gong X W, Wang J L,et al.Foliar water uptake improves branch water potential and photosynthetic capacity in Calligonum mongolicum [J].Ecological Indicators,2023,146:109825. |
| 50 | Li J, Hu S J, Sheng Y,et al.Whole-plant water use and hydraulics of Populus euphratica and Tamarix ramosissima seedlings in adaption to groundwater variation[J].Water,2022,14(12):1869. |
| 51 | Cui Y Q, Niu L Q, Xiang J L,et al.Water uptake from different soil depths for desert plants in saline lands of Dunhuang,NW China[J].Frontiers in Environmental Science,2021,8:585464. |
| [1] | 陆忠奇, 赵竹君, 何清. 库尔勒市大气颗粒物浓度特征及来源[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(6): 74-84. |
| [2] | 李汉林, 何清, 赵权威. 喀什地区PM10输送路径及潜在源区[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(5): 62-70. |
| [3] | 董莹, 华中, 陆志翔, 许宝荣, 邹松兵. 面向低碳转型的甘肃省地区聚类分析[J]. 中国沙漠, 2020, 40(5): 25-31. |
| [4] | 赵玉, 冯起, 李会亚. 黑河下游土壤盐分分布特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2017, 37(6): 1196-1203. |
| [5] | 李辉霞, 周红艺, 魏兴琥. 基于RUE和NDVI的人类活动对植被干扰强度分析——以桂西北为例[J]. 中国沙漠, 2014, 34(3): 927-937. |
| [6] | 安帅, 王乃昂, 陈会丽, 赵力强. 基于SOFM网络的巴丹吉林沙漠湖泊聚类及其地下水补给来源推断[J]. 中国沙漠, 2014, 34(2): 574-581. |
| [7] | 李 磊1,2,3, 李向义1,3, 徐新文1, 林丽莎1,3, 曾凡江1,3, 陈凤丽1,2. 策勒绿洲21种豆科牧草叶绿素荧光参数比较[J]. 中国沙漠, 2013, 33(5): 1363-1370. |
| [8] | 姜大海;王式功;尚可政. 沙尘暴危险度的定量评估研究[J]. 中国沙漠, 2011, 31(6): 1554-1562. |
| [9] | 任珺, 陶玲. 中国沙漠植物区系相似性的数值分析[J]. 中国沙漠, 2003, 23(3): 289-294. |
| [10] | 孙德祥, 蔡玉成, 刘旭. 多元统计分析法在树木水分生理研究中的应用[J]. 中国沙漠, 1993, 13(1): 28-34. |
| [11] | 李胜功. 樟子松适宜气候生态区的模糊聚类分析[J]. 中国沙漠, 1991, 11(3): 61-66. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
©2018中国沙漠 编辑部
地址: 兰州市天水中路8号 (730000)
电话:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
